MATLAB Basics
MATLAB Installation
Please follow the official MATLAB installation guide provided by your school to install and activate the MATLAB software.
Using MATLAB
In this section, I will demonstrate basic MATLAB operations using an example of reading and visualizing audio recording files. After installation, launch the MATLAB interface and use the cd command to navigate to your working directory.
Since repeatedly pasting commands in the command window is inconvenient for editing, we can create a ".m" script file to write and run code more efficiently. Click the "New" button at the top-left corner of the application, and select "Script":
An "Untitled.m" file will appear in the Editor. Click the save icon at the top-left, name the script, and save it in the current working folder. I have named it "Hello.m":
To facilitate processing of audio recordings, copy the ".wav" audio file recorded on your phone into the current MATLAB working directory.
In "Hello.m", write the following code to read and display the audio data:
% Read data and sampling frequency from the audio file receive.wav
[data, fs] = audioread('receive.wav');
% Plot the data in a figure
figure;
plot(data);
MATLAB generates the plot:
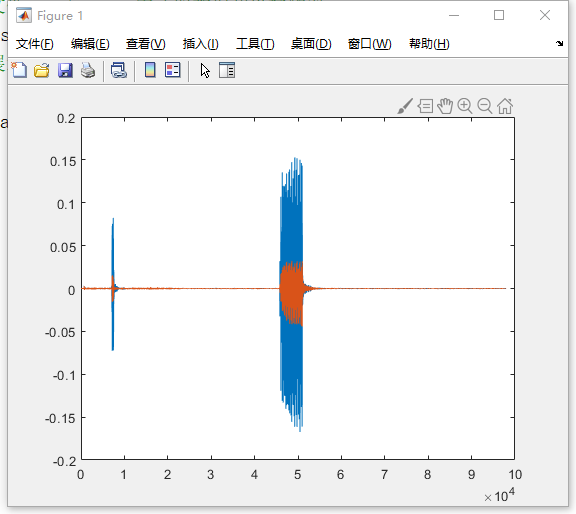
The x-axis represents sample point indices, and the y-axis represents amplitude values of the sound signal. After zooming in locally, the waveform appears as follows:
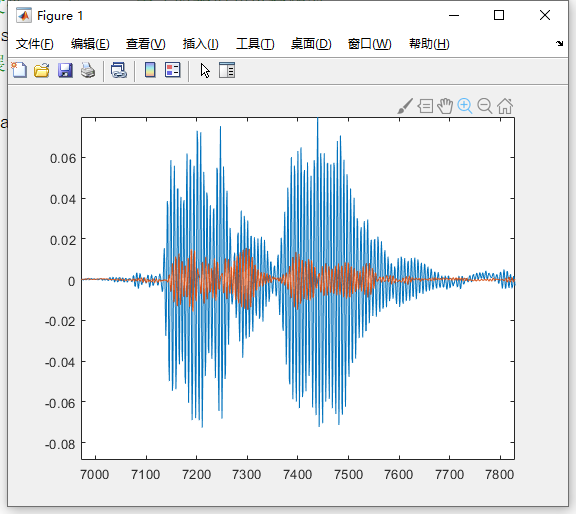
We can observe that two data lines are plotted—this is because the audio file contains dual-channel signals recorded by two microphones on the phone. Checking the variable data in the Workspace reveals it is an n×2 matrix:
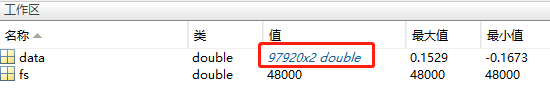
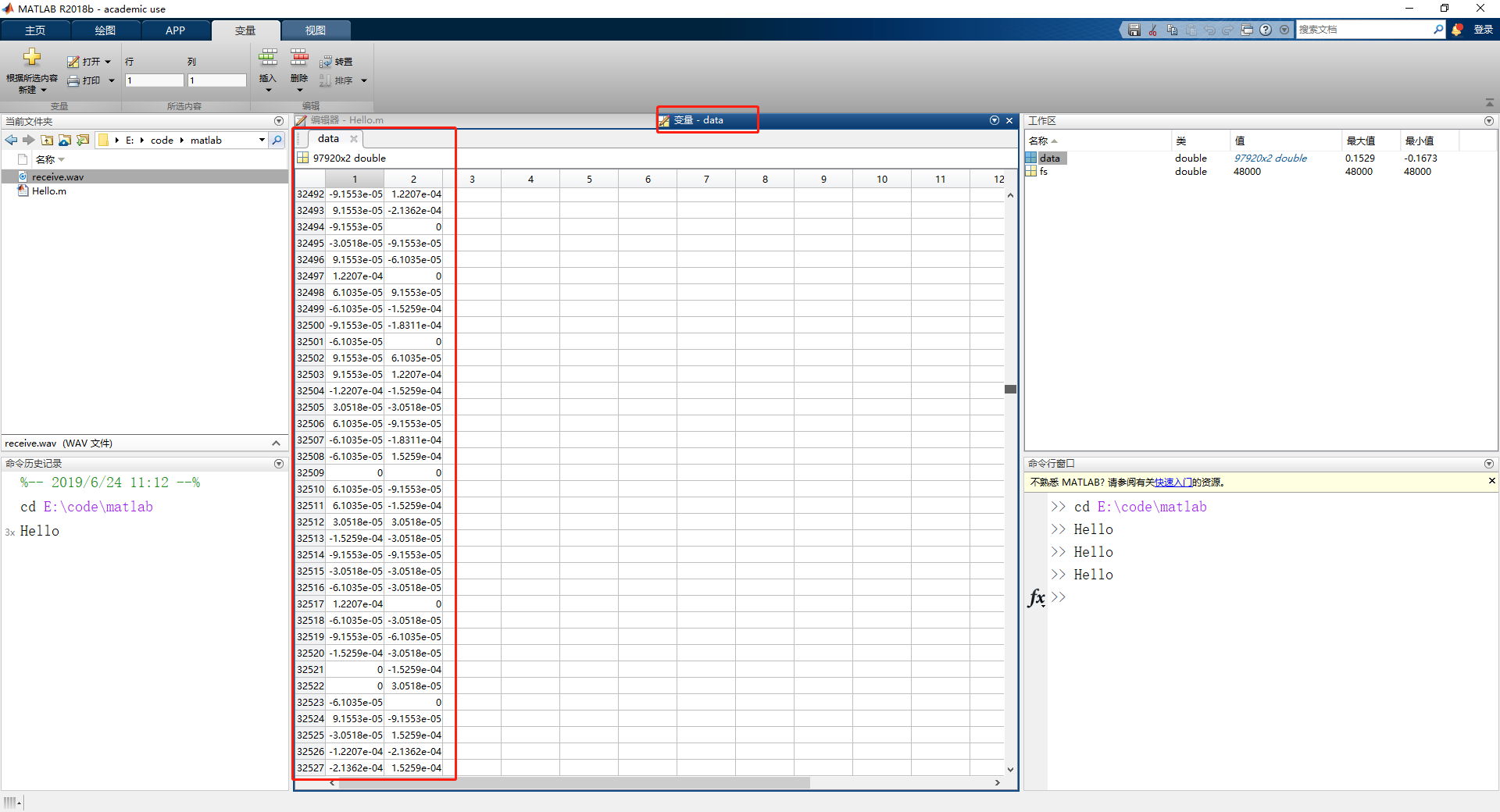
Double-clicking the variable name opens it in the Variable Editor, where you can scroll through its values:
Besides script files, MATLAB also supports function files. Click "New" → "Function":
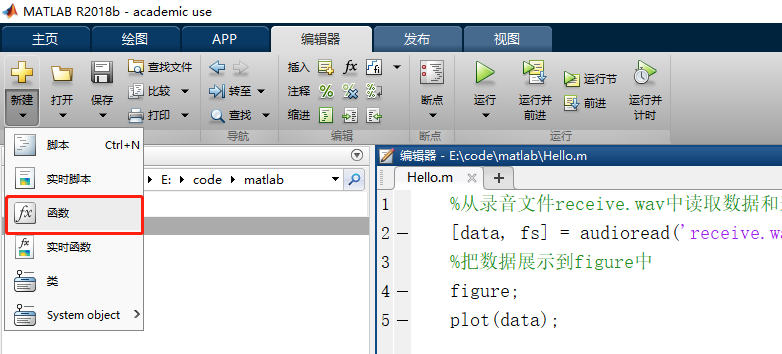
An unnamed .m file with an initial function structure appears in the Editor. Save the file with a chosen name. After saving, ensure that the function name matches the file name:
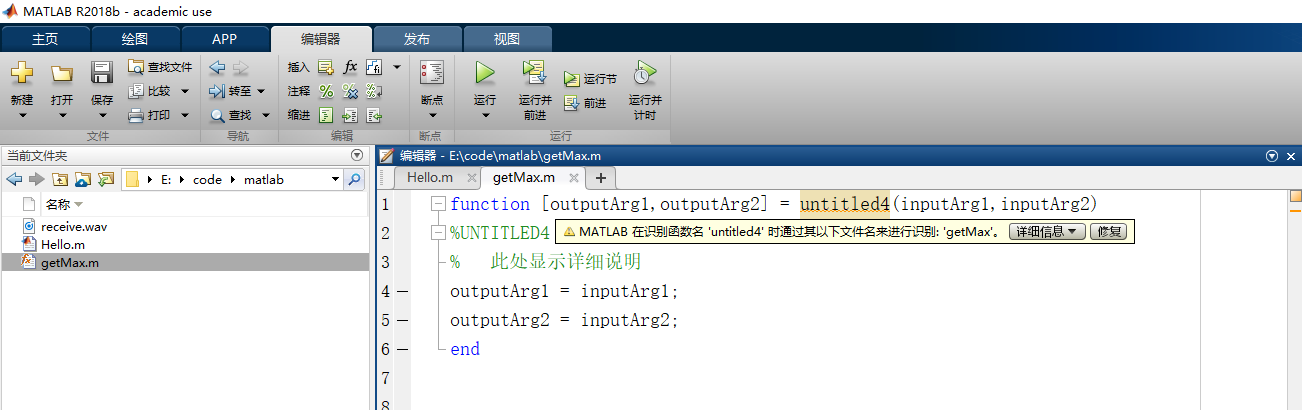
Once the function name is corrected, the small square indicator on the right side of the Editor turns green, indicating the issue is resolved.
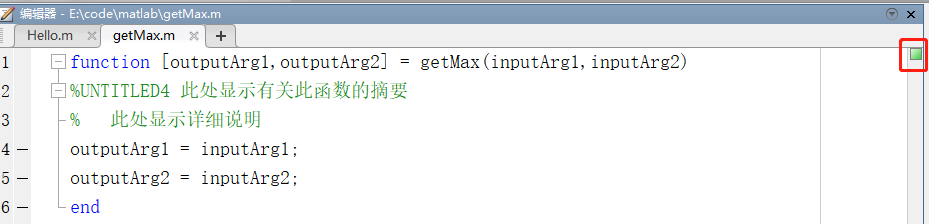
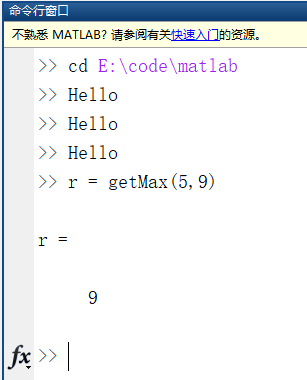
You can now modify the input/output arguments and computation logic according to your needs:
function [result] = getMax(a,b)
%getMax Brief description of this function
% Takes two numbers a and b as inputs, returns the maximum value.
result = max(a,b);
end
With these fundamentals, you are now ready to perform basic tasks in MATLAB. You are encouraged to explore further on your own. In our subsequent tutorials, new operations will be introduced when they are first used.